Programs
Experience
Services
Educator Topics
Subscribe to the Newsletter
Subscribe to the Blog

Federal funding is made available through formula funds and competitive funds.
Formula funds - also called allocated amounts or block grants - are distributed based on a predetermined formula, such as the number of low socio-economic status (SES) students at a given school or district.
Competitive funds - or discretionary grants - are awarded to eligible schools, districts, or other entities who apply by responding to an RFP, or request for proposal. The RFP response must describe in detail the need and purpose for using the funds based on the specifics of the application.
Coronavirus funds - Several coronavirus-related funding opportunities are available for ST Math. These include portions of the CARES Act as well as flexibilities that allow schools or districts to repurpose existing funding.

Meeting the Moment: The ST Math Buyers’ Guide

E-book: How to Accelerate Learning with Neuroscience

E-book: Demanding More From EdTech Evaluations

E-book: What Is Math Rigor?
It May Not Mean What You Think It Means

E-book: Bridge the Math Achievement Gap for English Learners

E-book: Rethinking Student Engagement
In the following pages, we'll answer the question of why we're stuck, and offer a way to move forward in our thinking about student engagement. In doing so, we'll also examine why student engagement isn't exactly what we should be striving for, and what we should actually be focusing on in order for students to learn deeply and truly build conceptual understanding.

E-book: Digital Manipulative Toolkit

Better Blends With Visual Game-Based Math
Blended learning involves a setting where students spend part of their instructional time with digital curricula and part of their time learning in a brick-and-mortar setting. Students also have some choice in which content they use, how quickly they go through it, where they do it, and for how long. Schools implement blended learning in a variety of ways and using various types of technology and curricula.

Recipe for Success in Gaining Momentum with Math
Appreciating the landscape of mathematics education today and the challenges of teacher shortages, math confidence in learners and teachers can help administrators build strong learning environments in math classrooms and establish math cultures in buildings. Math intervention solutions may be abundant, but an intervention is a short-term solution to a long-term issue. Utilizing neuroscience research to build the right environment for learning math is the optimal solution for long-term academic success.

Uncertain Role of Ed Software in Remediating Student Learning

ST Math White Paper: The Art of Facilitation

Spatial-Temporal Math:
Underlying Scientific Concepts and Mechanisms

Randomized Trial of Elem. School
ST Math Software Intervention Reveals Significant Efficacy
A randomized controlled trial group design study funded by IES NCR Grant R305A090527 was conducted in which 16,307 3rd, 4th, and 5th-grade students in 52 school grade-level clusters were randomly assigned to receive ST Math (program revision generation 3), a supplemental mathematics software instructional program, or to a business-as-usual mathematics instruction control.

The ST Math Theory of Change
How does student time and energy invested in ST Math result in schoolwide math proficiency gains? When students solve their way through the puzzle-based games, they self-pace through their grade-level math content and master mathematical concepts. Each ST Math learning objective completed aligns with state math standards, and each additional standard covered gives ST Math students a proven advantage on standardized assessments.
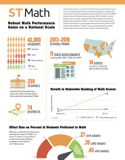
WestEd Study: Robust Math Performance Gains on a National Scale
Independent education research firm WestEd recently published the largest ever cross-state study evaluating a math edtech program on multiple state assessments.
Game-Based Math Infographic

Music and ST
(Spatial Temporal) Performance

STAR Treatment Effect on Mathematics

The Music- Math Connection

Music Training and Spatial Temporal

Enhanced Learning Research

The Joy of Learning Math Through Music
Investigating Spatial Correlates of Music Listening and Spatial-Temporal Processing

Non-Language-Based Instruction in Mathematics
A substantial barrier to early learning of mathematics arises from undeveloped language understanding. Research conducted by the MIND Institute (www.mindinstitute.net) has investigated new methods of teaching that don't rely on language proficiency.

ALAS White Paper: Math and Science

DA ED Talk: Empowering Diverse Students in Mathematics
Empowering Diverse Students in Mathematics: A Pathway to Equity and Excellence
In her quest to foster equity in education, focusing on mathematics, Dr. Kimberly Clark Moss, Coordinator of Educational Technology with Birmingham City Schools (AL), will explore how to level the playing field through engagement, motivation, and support.

EdWeek Webinar: Understanding And Applying The Science of Learning Math
Understanding And Applying The Science of Learning Math
The science of learning math, an approach that focuses on how students' brains learn, is backed by decades of research and evidence. In this panel discussion, leading math researchers and practitioners will define what the science of learning math is, why it is so effective, and what this looks like when applied in the classroom.
This NSF competitive funding opportunity seeks to significantly enhance the learning and teaching of science, technology, engineering, mathematics and computer science (STEM) by preK-12 students and teachers, through research and development of STEM education innovations and approaches. Projects in the DRK-12 program build on fundamental research in STEM education and prior research and development efforts that provide theoretical and empirical justification for proposed projects. Projects should result in research-informed and field-tested outcomes and products that inform teaching and learning.
ITEST supports projects that engage students in technology-rich experiences that: (1) increase awareness of and interest in STEM and ICT occupations; (2) motivate students to pursue appropriate education pathways to those occupations; and (3) develop STEM-specific disciplinary content knowledge and practices that promote critical thinking, reasoning, and communication skills needed for entering the STEM and ICT workforce of the future.
STEM+C supports research on how students learn to think computationally to solve interdisciplinary problems in science and mathematics. The program supports research and development that builds on evidence-based teacher preparation or professional development activities that enable teachers to provide excellent instruction on the integration of computation and STEM disciplines. Proposals should describe projects that are grounded in prior evidence and theory, are innovative or potentially transformative, and that will generate and build knowledge about the integration of computing and one or more STEM disciplines at the preK-12 level.
AISL seeks to advance new approaches to and evidence-based understanding of the design and development of STEM learning opportunities for the public in informal environments; provide multiple pathways for broadening access to and engagement in STEM learning experiences; advance innovative research on and assessment of STEM learning in informal environments; and engage the public of all ages in learning STEM in informal environments.
Funds are granted for charitable, scientific, literary or educational purposes or for the identification, ongoing evaluation, education of and services for children and adults with learning disabilities.
To increase understanding and expertise in fostering support of multi-language development when teaching mathematics. The proposed project must explicitly support the implementation of equitable and rigorous mathematics teaching that incorporates students' languages and cultures in their learning of mathematics.
To encourage the innovative use of technology and other tools to "help teachers and students visualize and concretize mathematics abstractions..." (Principles to Actions). When used appropriately, they can enhance other effective teaching and promote meaningful learning opportunities for students. The focus of the proposal should be on the mathematics being taught and innovative uses of the tools and technology.
Title III ensures language instruction for limited English proficient and immigrant students.
In traditional math education, ELs can miss out on crucial opportunities to understand the meaning behind the math. Because so much of traditional math materials are word-heavy, there are language hurdles EL students must overcome before they can even begin to focus on math concepts. With the ST Math visual instructional program, language barriers are removed, giving ELs access to the same level of math rigor as other students.
The headline and subheader tells us what you're offering, and the form header closes the deal. Over here you can explain why your offer is so great it's worth filling out a form for.
Remember:
MIND Research Institute and our philanthropic partners are dedicated to ensuring that all students are mathematically equipped to solve the world's most challenging problems.
The ST Math School Grants Program provides funds to our education partners to help cover the cost of the program. We have over $1,000,000 in funding from our partners to help us reach the next 1,000,000 students.
Currently approximately 20% of ST Math schools receive donor funding from MIND’s philanthropic partners.


A significant amount of education funding is provided at the state and local level through income tax, sales tax, and more. State funding initiatives that approve ST Math include but are not limited to:
The MIND Research Institute team can be of assistance as you navigate the landscape of state and local funds that are available to you. Tell us more about your needs and our team would be pleased to assist.
Get Funding Support